In the Archives: Last Train to Carp-ville
Berlin-born Sonoma, California aquapreneur Julius Poppe chaperoned his group of 83 passengers on board a steamer moored in Bremen, Germany. The 12-day journey to New York that summer of 1872 proved deadly. After arrival and a two-day quarantine, only 8 of Poppe’s charges survived.
Poppe settled them onto a train. The Transcontinental Railroad linking the West Coast to Iowa and the eastern rail network had been completed only three years earlier. Despite Poppe’s best efforts for those in his care, two more died in San Francisco, and another died on the boat from San Francisco to the coast near Sonoma.
Five had survived the nearly 7,000-mile journey – only the youngest, each about the size of a pen. Poppe placed them in his pond that August, hoping for their survival.
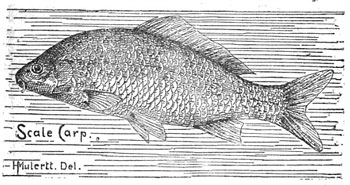
By the following May, the five German carp, also known as scale or common carp, had spawned 3,000 young. They also helped spawn a short-lived nationwide carp craze. In Michigan, state fish officials’ initial enthusiasm turned to alarm as the non-native’s depredations became another one of the state’s late 19th-century ecological disasters. [Full Story]