Tree Town OKs Urban Forestry Plan
The city’s first comprehensive plan for managing Ann Arbor’s urban forest has been given approval by the city council. Action came at the council’s June 2, 2014 meeting. The Ann Arbor park advisory commission had recommended adoption of the plan at its meeting on April 15, 2014. [.pdf of Urban & Community Forest Management Plan]
An urban forest is defined as all the trees, shrubs and woody vegetation growing along city streets, in public parks and on institutional and private property. In Ann Arbor, about 25% is on public property, with 75% on private property. Based on a U.S. Dept. of Agriculture Forest Service i-Tree Eco Analysis done in 2012, Ann Arbor’s urban forest has an estimated 1.45 million trees. It creates a 33% tree canopy – the layer of leaves, branches and stems of trees that cover the ground when viewed from above.
The city manages 43,240 street trees and about 6,900 park trees in mowed areas. A tree inventory conducted in 2009 didn’t include natural areas, she noted, so there are thousands of trees that aren’t counted. The urban forest includes over 200 species, representing 82 genera.
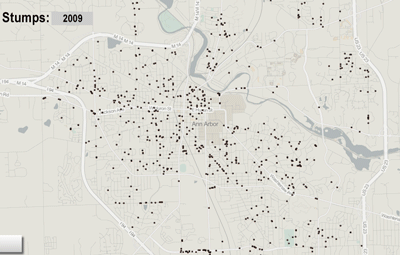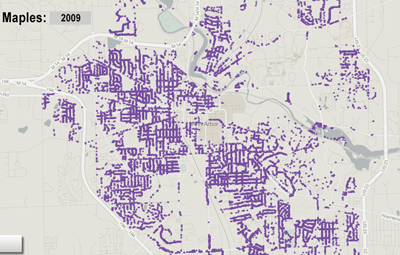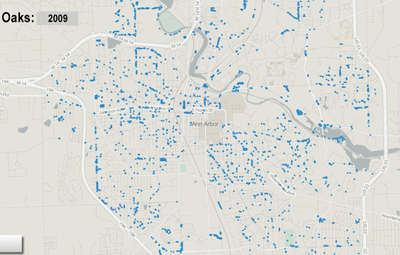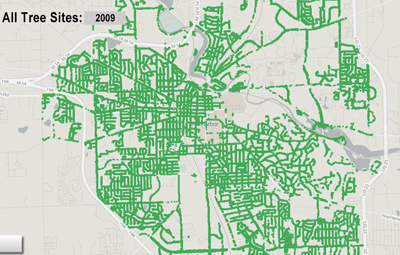
Map of selected tree variety by The Chronicle from city of Ann Arbor 2009 survey. Image links to dynamic map hosted on geocommons.com
PAC had been briefed on the 135-page Urban & Community Forest Management Plan at its Feb. 25, 2014 meeting by Kerry Gray, the city’s urban forest & natural resources planning coordinator. The management plan includes 17 recommendations, listed in priority based on community feedback for implementation. Each of the 17 recommendations includes action tasks and implementation ideas, case studies, and resources that are needed, including funding. The recommendations are:
- Implement proactive tree maintenance program.
- Strengthen tree planting and young tree maintenance programs.
- Monitor threats to the urban and community forest.
- Increase landmark/special tree protections.
- Secure adequate city‐funding for urban forestry core services.
- Develop street tree master plans.
- Pursue grant and philanthropic funding opportunities.
- Strengthen forestry related ordinances.
- Update tree inventory and canopy analysis.
- Develop urban forest best management practices.
- Increase urban forestry volunteerism.
- Strengthen relationships with outside entities who impact trees.
- Implement community outreach program.
- Obtain the best use of wood from removed trees.
- Create city staff working groups to coordinate projects that impact trees.
- Engage the city’s Environmental Commission in urban and community forestry issues.
- Review the urban forest management plan periodically and update as needed.
The city council has adopted a budget for FY 2015, which starts July 1, 2014 that includes a one-time expenditure of $1 million to address the backlog in maintenance of trees in the public right of way.
Included in the focus of the effort to remove the back log are trees classified as Priority 1 removals (red dots), Priority 2 removals (yellow dots), Priority 3 removals (blue dots) for large trees and Priority 1 prunings (green dots) [Map by The Chronicle with data from the city of Ann Arbor.]:
This brief was filed from the city council’s chambers on the second floor of city hall, located at 301 E. Huron.